Essential Zinc
ZINC
%
Living Things that Require Zinc
FACTS
# of Enzymes in Human Body Requiring Zinc
ZINC IS ESSENTIAL FOR LIFE
Zinc is one of nature’s most vital, essential elements. Humans, animals, plants, and even the smallest micro-organisms need zinc. There is no life without zinc. Zinc is in all parts of our body; it is in our organs, tissues, bones, fluids, and cells. Because zinc is used to generate cells, it is especially important during pregnancy, for the growing fetus whose cells are rapidly dividing. And zinc is vital in activating growth (height, weight and bone development) in infants, children, and teenagers. Among all the vitamins and minerals, zinc shows the greatest effect on our immune system. Zinc helps fight infections and can even reduce the duration and severity of the common cold. Zinc also enhances memory and thinking by interacting with other chemicals to send messages to the sensory brain center. Zinc can also reduce fatigue and mood swings. Zinc is vital for taste and smell; it is needed for the renewal of skin cells; and it helps keep our hair and nails healthy.
Among all the vitamins and minerals, zinc shows the strongest effect on our all-important immune system.
Zinc has proven effective in helping fight infections and can even reduce the duration and severity of the common cold.
Ensuring adequate levels of zinc intake should be a key component in efforts to reduce child illness, enhance physical growth and decrease mortality in developing countries.
The International Zinc Association, on behalf of the zinc industry, is taking a global lead in advocating for programs aimed at addressing zinc deficiency.
Dietary Sources of Zinc & Their Average Zinc Content
| Oysters | 25 |
| Meat (especially red meat) | 5.2 |
| Nuts | 3.0 |
| Poultry | 1.5 |
| Eggs | 1.3 |
| Milk Products | 1.2 |
| Cereals | 1.0 |
| Bread | 1.0 |
| Fish | 0.8 |
| Green Vegetables | 0.4 |
| Potatoes | 0.3 |
| Fresh Fruits | 0.1 |
*Large doses of zinc should not be taken over a prolonged period without your physician’s direction.
EXPLORE HOW ZINC IS ESSENTIAL FOR LIFE
The human body contains 2-3 grams of zinc, one of nature’s essential elements in a balanced diet. Approximately two billion people are considered micro-nutrient deficient worldwide and complications due to zinc deficiency contribute to hundreds of thousands of childhood deaths annually. Due to linkages between insufficient zinc in the diet and healthy growth and development in children, the World Health Organization provides recommendations for minimum daily levels of zinc, guidelines for fortifying staple foods with zinc, and recommends zinc for treating acute diarrheal disease. Recommended daily intakes range from 5 mg (infants) to 15 mg (adult men); pregnant women and lactating mothers also require more zinc to ensure optimal development of the fetus and newborn baby.
Find out more by selecting a system of the body.
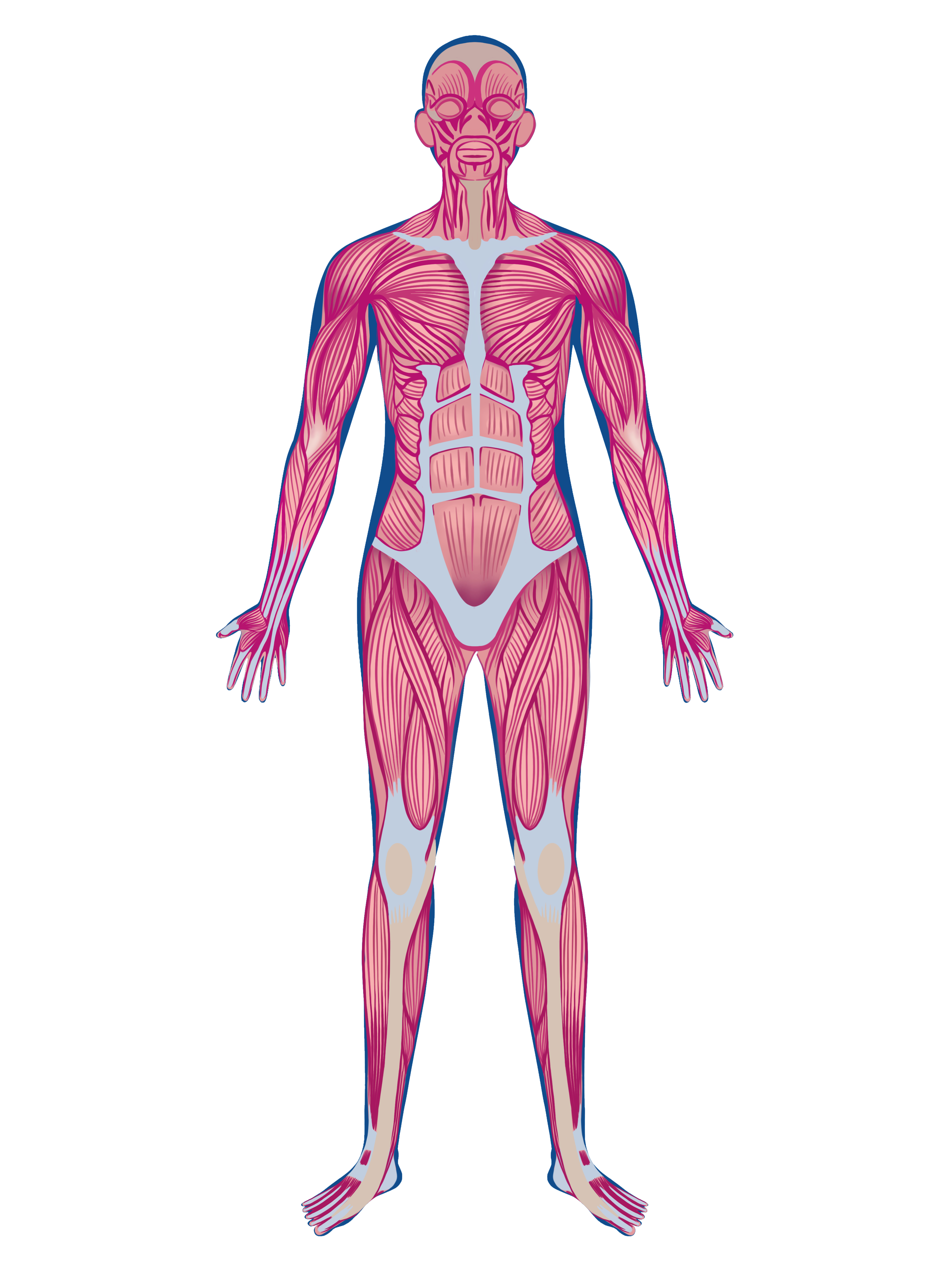
Muscular
Zinc is vital for various aspects of muscular system function, including muscle contraction, energy production, protein synthesis, antioxidant defense, and hormonal regulation. A deficiency in zinc can lead to muscle weakness, fatigue, and impaired muscle repair.
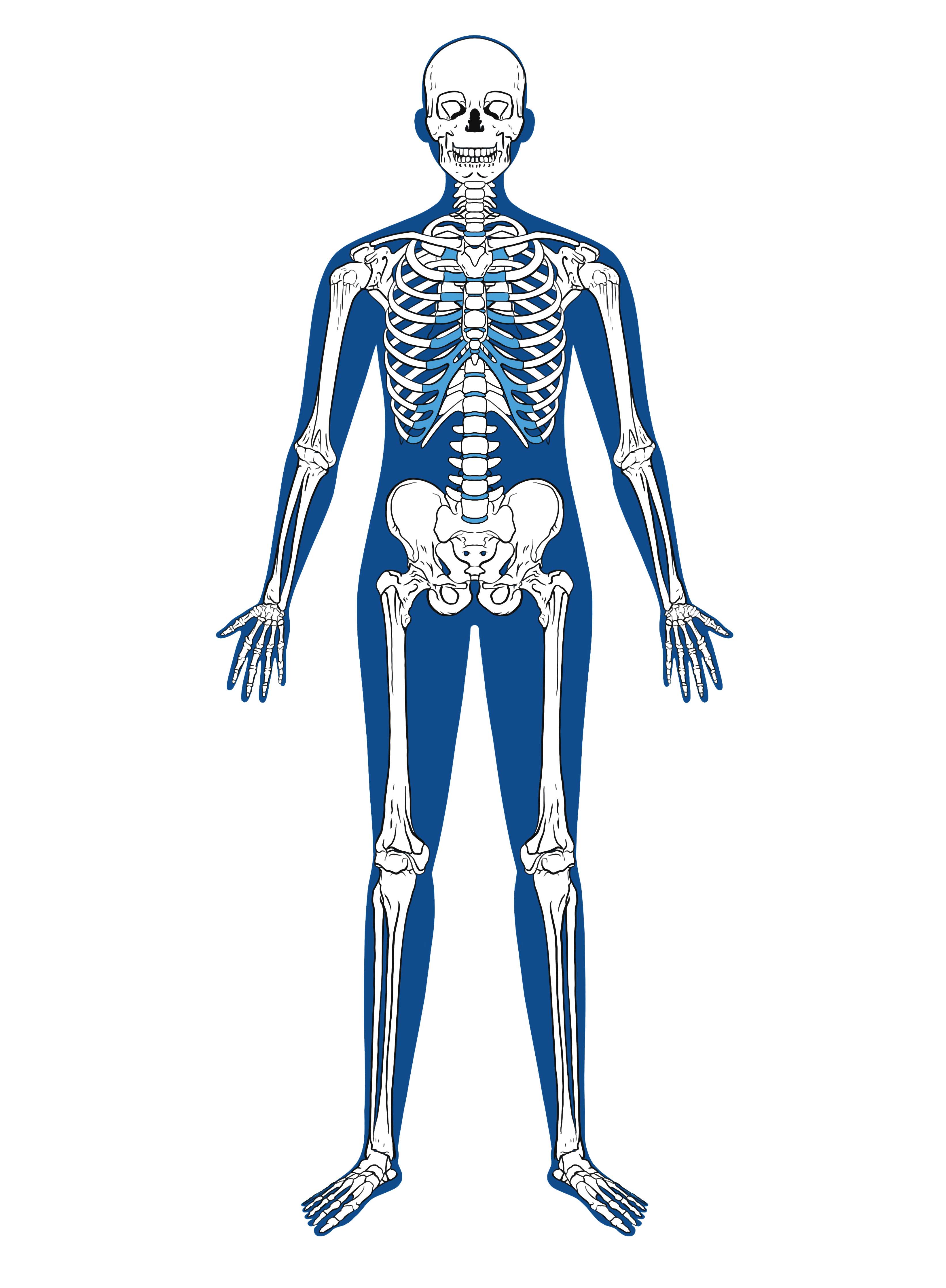
Skeletal
Zinc is vital for various aspects of skeletal system function, including bone formation, mineralization, strength, calcium absorption, hormonal regulation, and antioxidant defense. A deficiency in zinc can lead to impaired bone growth, reduced bone density, and an increased risk of fractures.
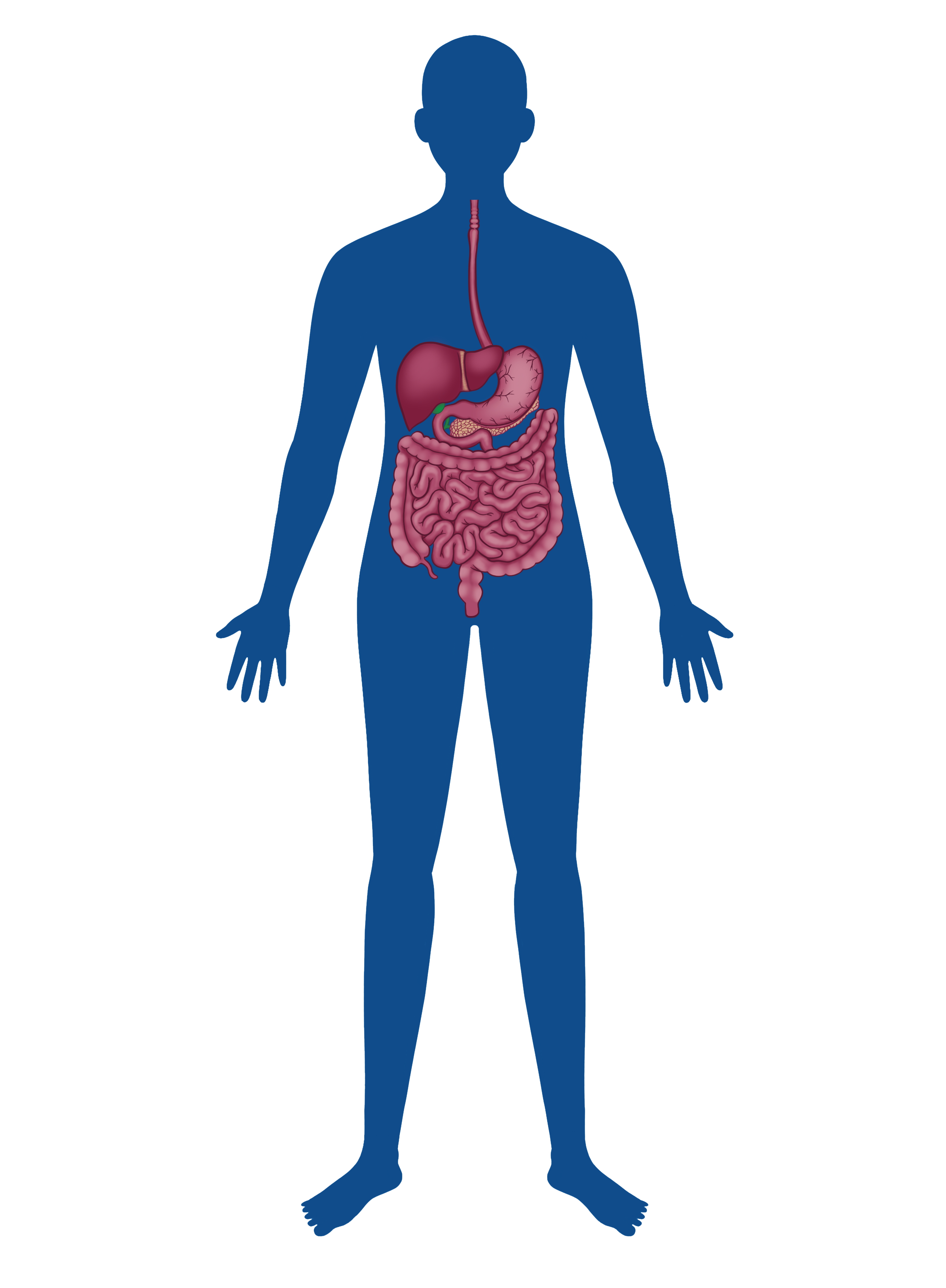
Digestive
Zinc is vital for various aspects of digestive system function, including enzymatic functions, gastric acid production, protein synthesis, immune function, and nutrient absorption. A deficiency in zinc can lead to impaired digestion, malabsorption of nutrients, and increased susceptibility to infections and inflammation in the gastrointestinal tract.
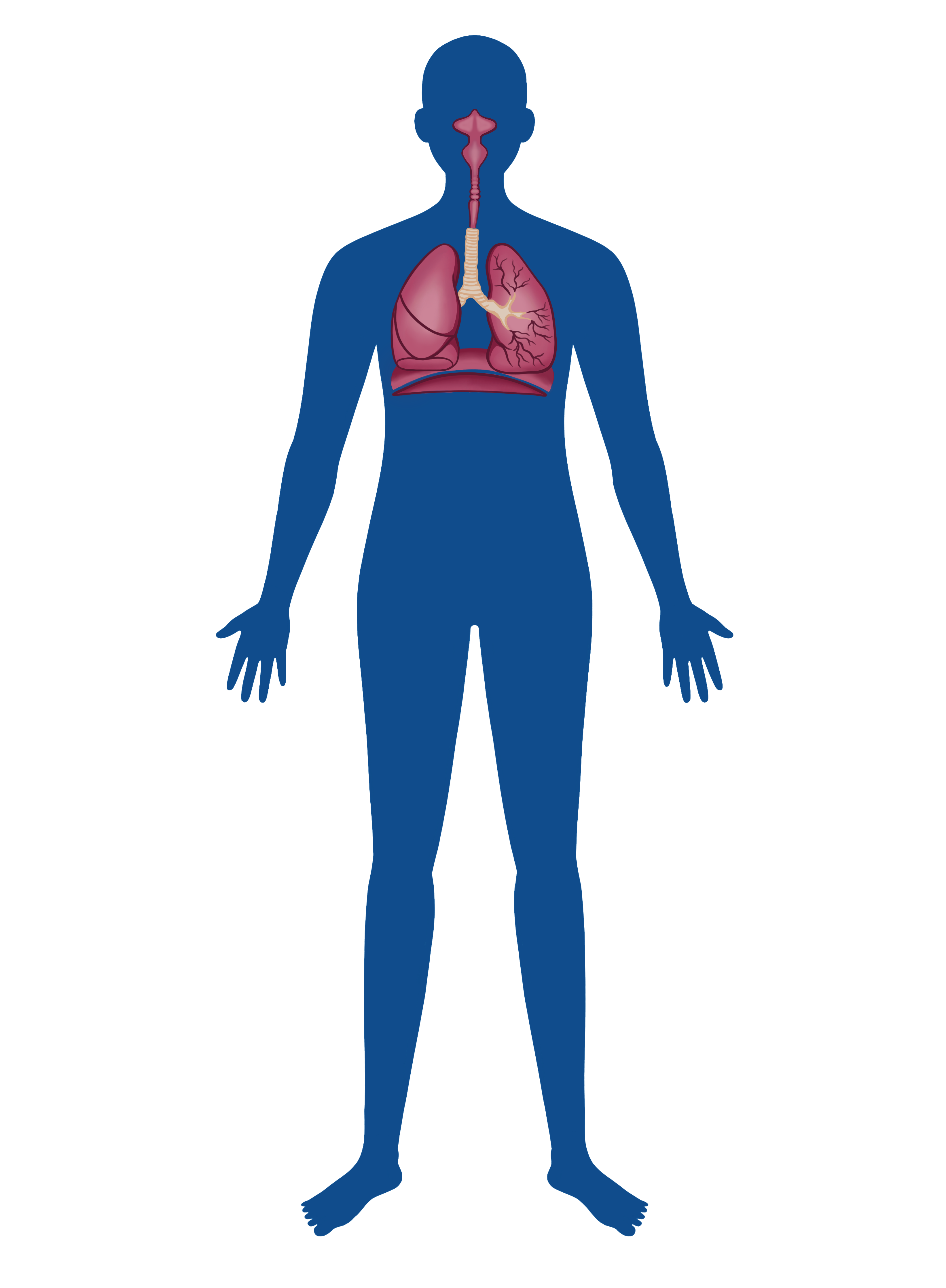
Respiratory
Zinc is vital for various aspects of respiratory system function, including immune function, antioxidant defense, mucosal integrity, wound healing and tissue repair, and ciliary function. A deficiency in zinc can impair the respiratory system's ability to defend against infections and may contribute to chronic respiratory conditions.
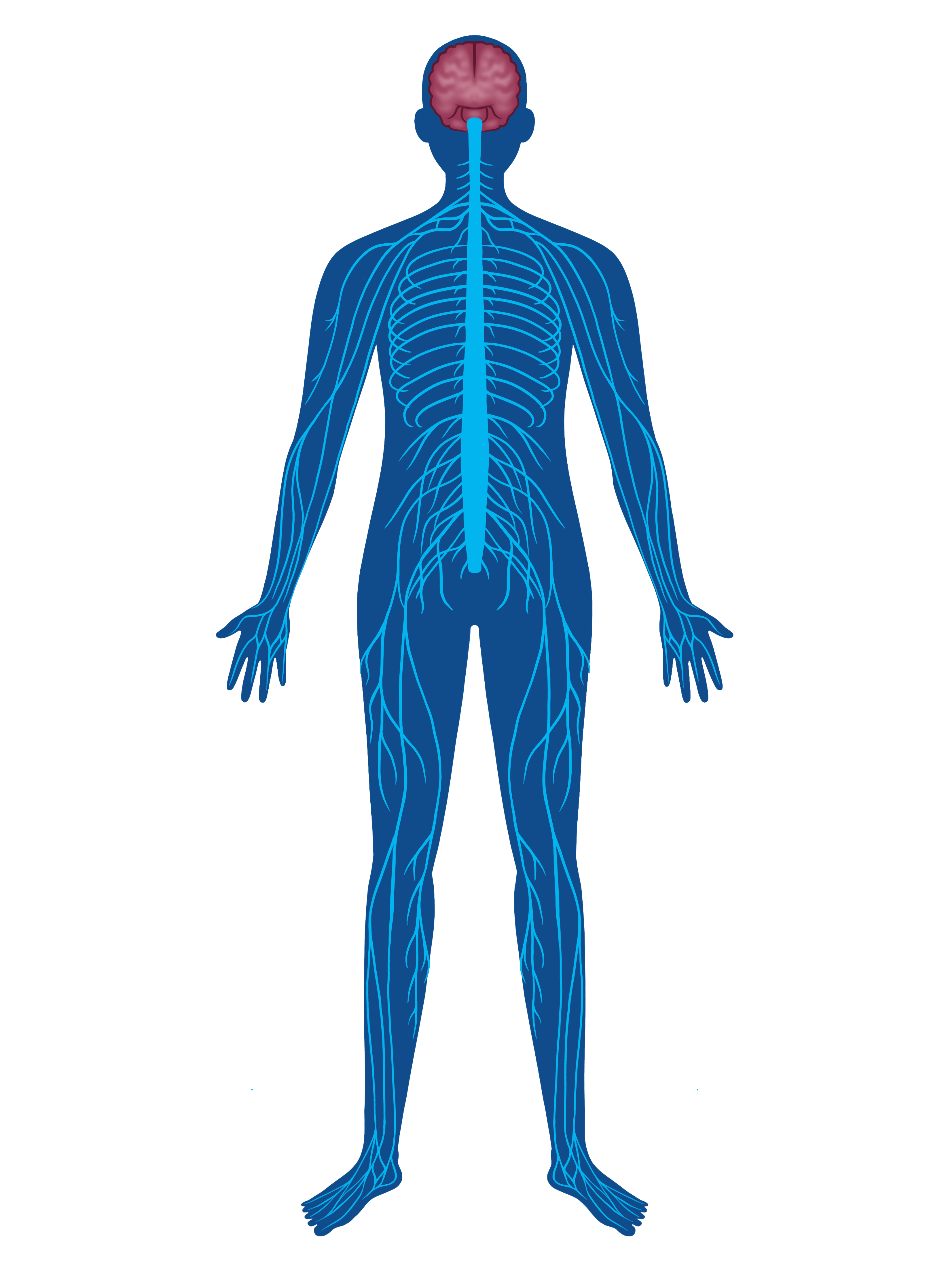
Nervous
Zinc is vital for various aspects of nervous system function, including neurotransmission, synaptic plasticity, neuronal growth and development, antioxidant defense, cognitive function, and mood regulation. A deficiency in zinc can lead to impaired cognitive performance, increased susceptibility to neurodegenerative disorders, and mood imbalances.
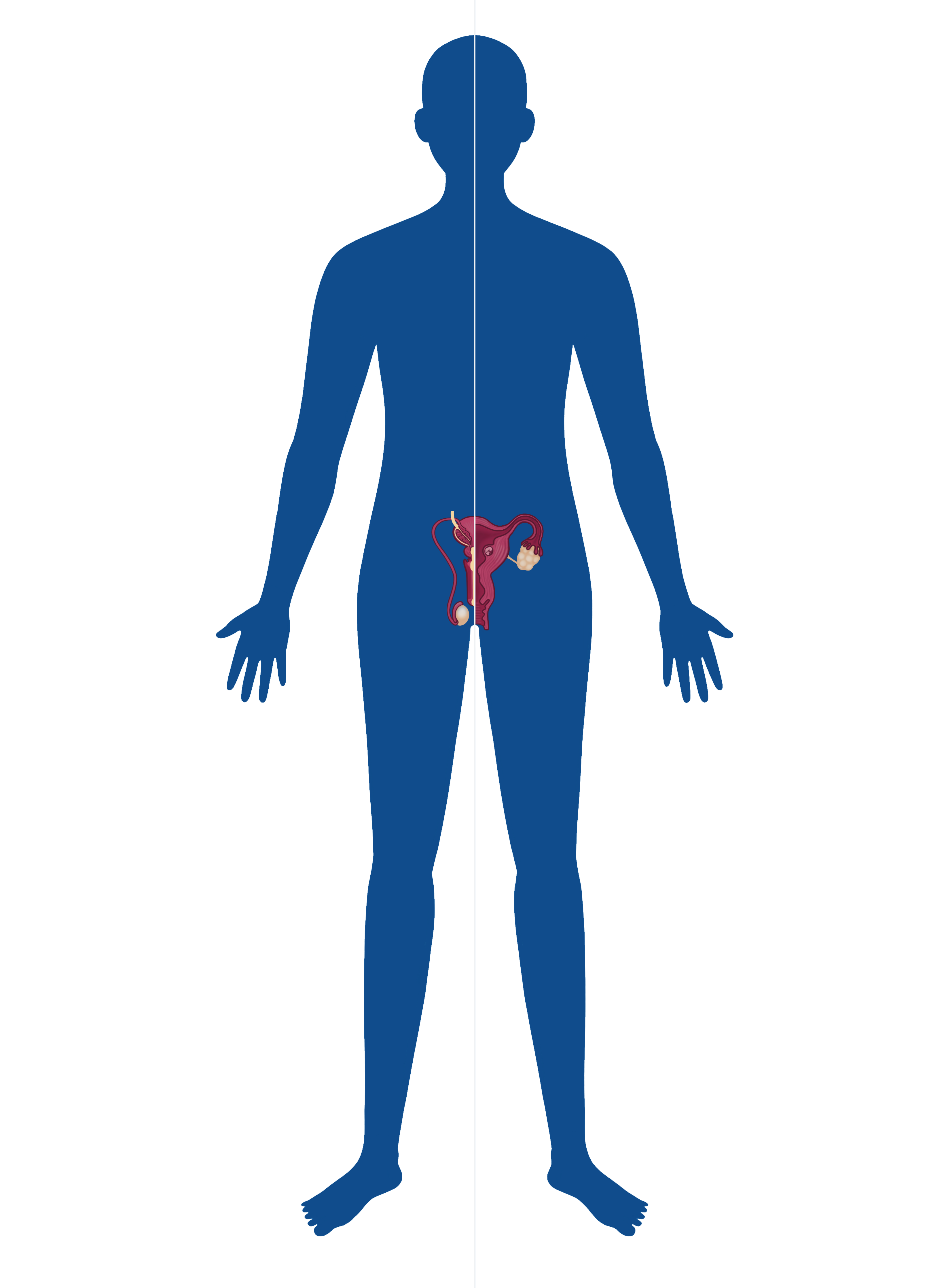
Reproductive
Zinc is vital for various aspects of reproductive system function, including hormonal regulation, sperm production and function, oocyte maturation and fertilization, embryonic development, immune function, and antioxidant defense. A deficiency in zinc can lead to impaired fertility, increased risk of reproductive complications, and adverse effects on fetal development.
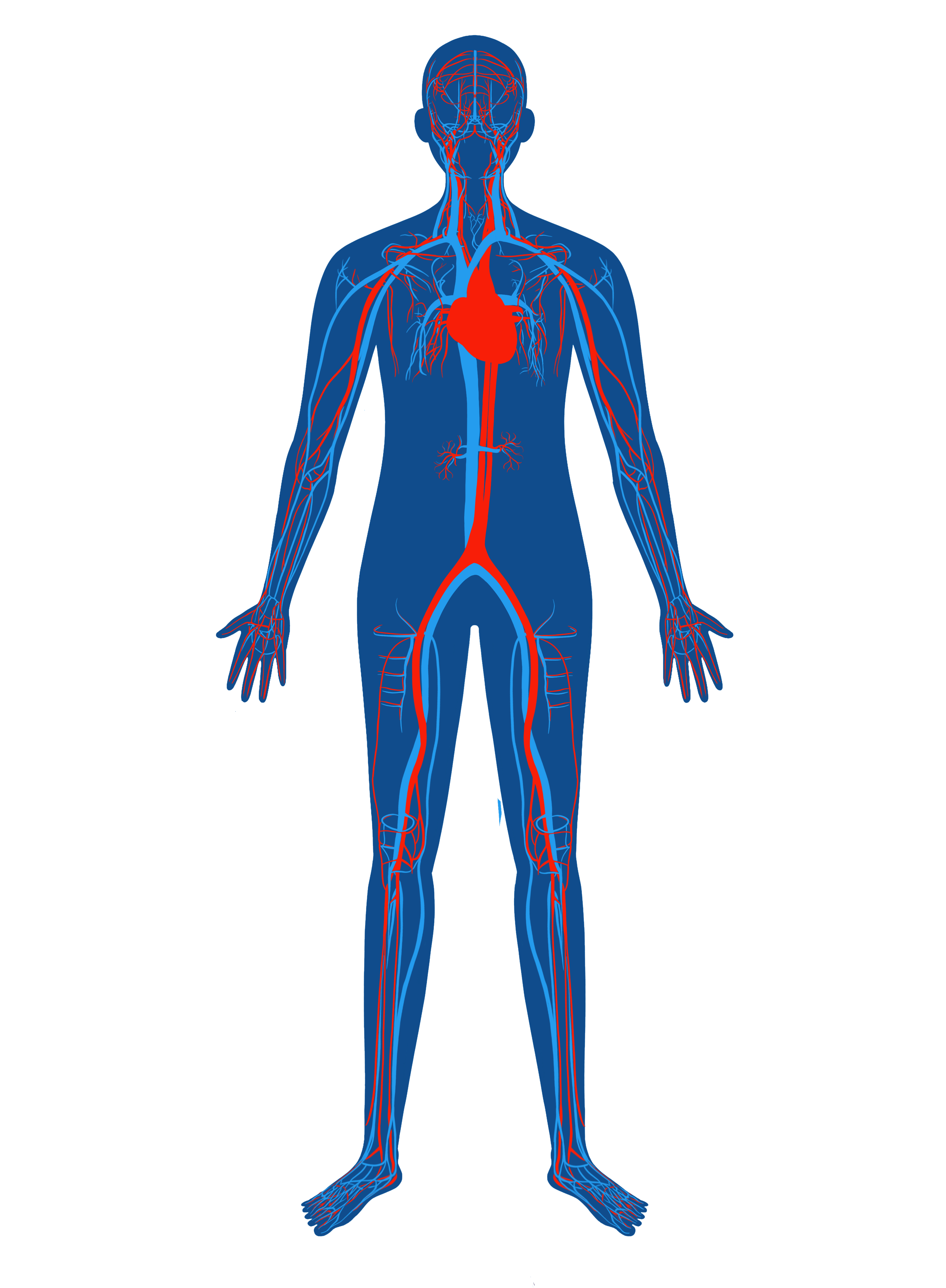
Cardiovascular
Zinc is vital for various aspects of cardiovascular system function, including vascular health, blood pressure regulation, antioxidant defense, anti-inflammatory effects, lipid metabolism, and cardiac function. A deficiency in zinc can contribute to the development and progression of cardiovascular diseases, such as atherosclerosis, hypertension, and heart failure.