Zinc Creates Long-Lasting, Sustainable Infrastructure
Building strong communities begins with building strong infrastructure designed to last for generations. In bridges, roadways, and sewer systems, zinc contributes to long-lasting, low-maintenance solutions that enhance durability, structural integrity, and environmental performance.
Through the Zinc Enables Decarbonization (ZED) initiative, the benefits of zinc in public infrastructure are rigorously quantified and substantiated. This research positions zinc as a critical, strategic material in the development of sustainable, low-carbon infrastructure to support safer and more financially secure communities.
Zinc's Value Proposition
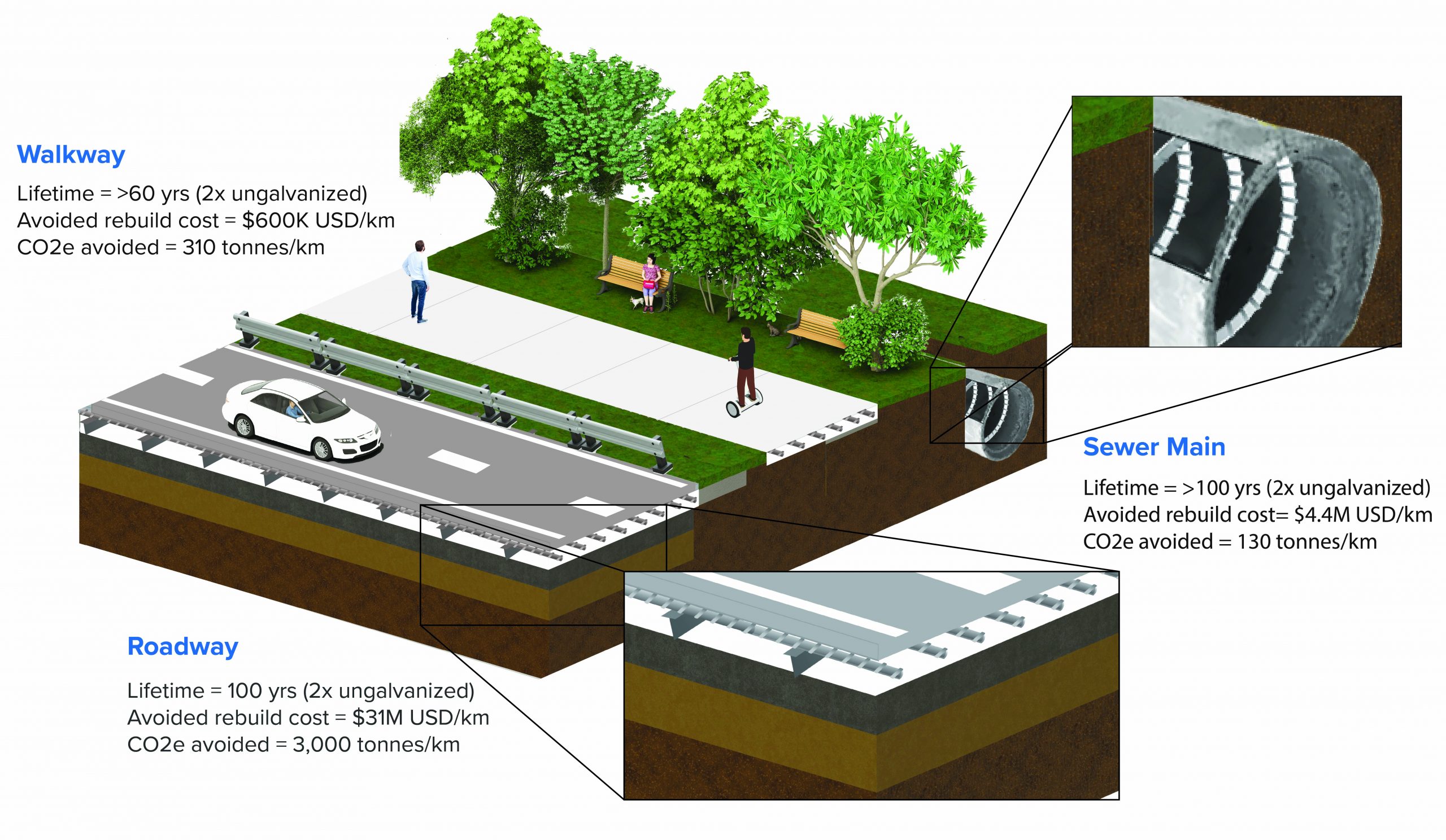
Zinc provides a cost-effective option for enhancing durability and sustainability in construction. By protecting steel from corrosion, zinc significantly extends its lifespan, reducing maintenance and replacement costs. By strengthening bridges, roadways, and sewer systems with galvanized rebar, zinc-coated steel bars designed to reinforce concrete structures, zinc ensures infrastructure lasts longer, offering many decades of reliable performance and environmental benefits.

Using galvanized steel rebar to reinforce roadways and bridges can extend lifespan more than 50 years.

Years
Using galvanized steel rebar to reinforce buried concrete sewer pipes can extend lifespan more than 50 years.

Years
Using galvanized steel rebar to reinforce a sidewalk can extend its lifespan more than 30 years.
Direct Costs
Strong communities need durable public infrastructure to support transportation and utility systems that stand the test of time. By protecting critical components like bridges, roadways, and sewer systems from corrosion-induced degradation, zinc reduces the direct costs associated with maintenance. Moreover, long-lasting public infrastructure minimizes material waste and the environmental impacts of repairs or replacements, contributing to lower carbon emissions and a reduced climate footprint.

USD
Avoided future cost to replace 1-km roadway when using galvanized steel rebar

USD
Avoided future cost to replace 1-km sewer main when using galvanized steel rebar

USD
Avoided future cost to replace 1-km walkway when using galvanized steel rebar
Carbon Emissions
Beyond zinc’s cost savings, building with zinc also prevents the carbon emissions associated with extracting, manufacturing, and transporting replacement materials and alleviates the financial pressures associated with escalating carbon prices. In this way, zinc supports both economic and environmental goals, providing a practical and scalable pathway toward decarbonization across industries.

tCO2e
Carbon emissions prevented over lifetime of 1-km roadway using galvanized rebar

tCO2e
Carbon emissions prevented over lifetime of 1-km sewer main using galvanized rebar

tCO2e
Carbon emissions prevented over lifetime of 1-km walkway using galvanized rebar
Zinc's Role In Reducing Embodied Carbon
As the construction industry embraces a low-carbon future, zinc stands out as a key material in tackling embodied carbon. By protecting materials, reducing waste, and enhancing recyclability, zinc not only reduces carbon emissions but also ensures more sustainable and resilient infrastructure built to last for generations.